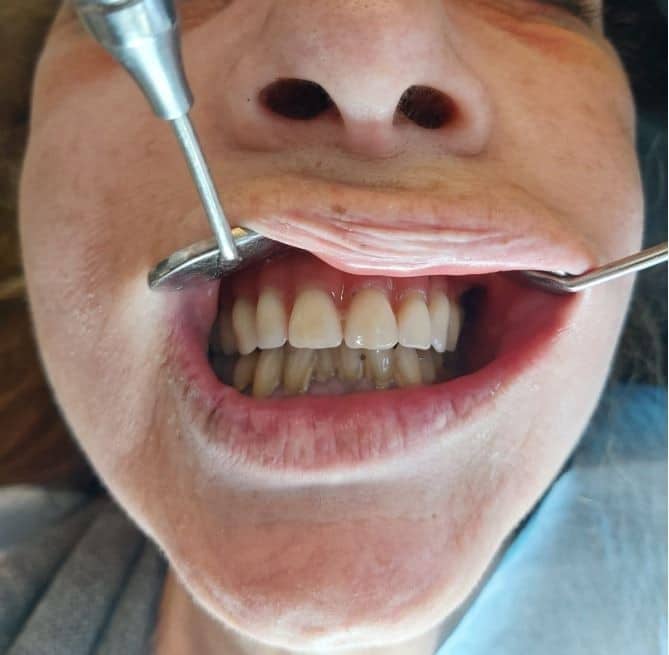
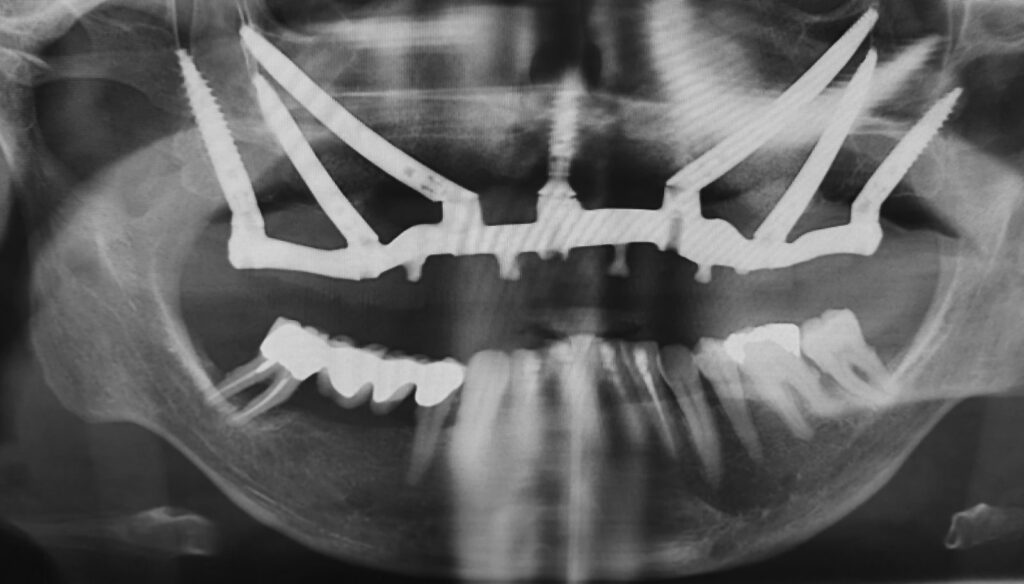
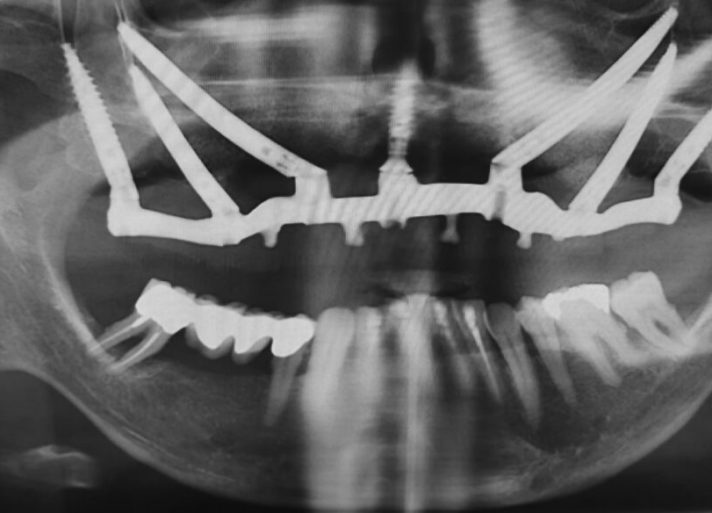
Full Arch Case of severe Atrophic Maxilla using the EZgoma® – Zygomatic Guided Technology
Surgeon: Prof. Ziv Mazor / Lab Tech: Gustavo Skladnik (DentexLab) / Surgery Planning: Noris Medical Digital Department
___________________________________________________
EZgoma® – Zygomatic Guided Technology enabling a quick precise minimally invasive Extra Maxillary and Intra Sinus drilling protocol execution for Zygomatic implants placement as well as Pterygoid and regular implants.
All components, Implants, and Prosthetics are directed by the guide to an accurate pre-planned position and orientation.
___________________________________________________
Introduction
Freehand execution of Zygomatic and Pterygoid implants require special knowledge skills and experience.
Unlike ridge related angles for regular implantation, Zygomatic implants angles are related to the Inferior Orbital rim, alveolar ridge, the maxillary sinus lateral wall and the Zygomatic bone itself. Pterygoid Implants angle trajectory is related to the tuberosity, the maxillary sinus and the medial plate of the sphenoid bone.
Both procedures are 3D angle trajectory-based and are challenging to perform.
Noris Medical EZgoma® (Patented) Guided technology enables a time-saving and accurate execution for the most complicated atrophic maxilla cases.
Noris Medical Zygomatic Implants and instrumentation greatly simplifies the Drilling Protocol and Implant and Prosthetic placement. High torque is consistently achieved, allowing immediate placement of a screw-retained prosthesis.
Clinical case
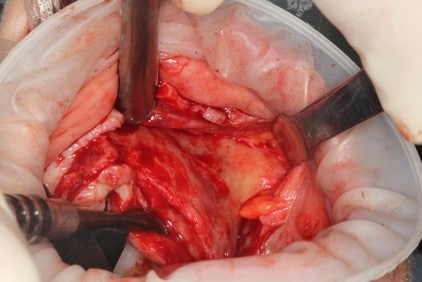
Female patient, 60 years old without major systemic disease.
Having edentulous atrophic maxilla[1], the maxilla presents severe bone resorption with defects in the area around the nasal spine, severe posterior ridge bone loss and narrow Zygomatic bone.
A Pre-op E.N.T specialist evaluation advised performing a FESS (Function Endoscopic Sinus Surgery) operation. The procedure was performed 3 months before the surgery [1.1]
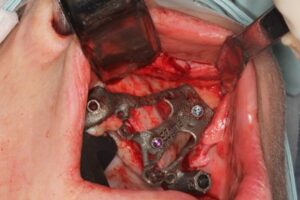
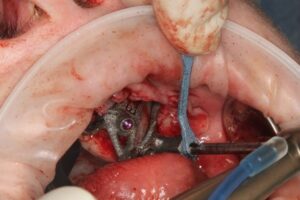
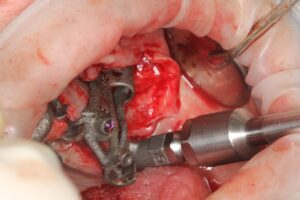
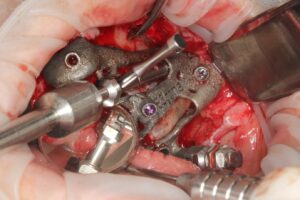
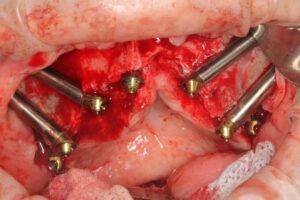
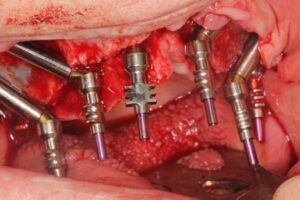
According to the clinical and radiographic examination CBCT, it was decided to install two Zygomatic implants and one Pterygoid on each side and one Lateral narrow implant in a lateral position for Screw-retained Prosthetic Rehabilitation. The procedure is done guided, Lateral implant will be placed freehand.
Planning Procedure
![[1] Severe Edentulous Atrophic Maxillary bone situation [1] Severe Edentulous Atrophic Maxillary bone situation](https://norismedical.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/1-1-1024x575.jpg)
![[1.1] Post-Op FESS (Function Endoscopic Sinus Surgery) operation 3 month prior to surgery. [1.1] Post-Op FESS (Function Endoscopic Sinus Surgery) operation 3 month prior to surgery.](https://norismedical.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2-1.jpg)
Surgery planning was done using the CT dicom that was available prior to the FESS operation.
![[2-3] Zygomatic and Pterygoid implants planned positions [2-3] Zygomatic and Pterygoid implants planned positions](https://norismedical.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/3-1-1024x325.jpg)
![[4-6] Implant positions are planned to support the desired screw-retained rehabilitation [4-6] Implant positions are planned to support the desired screw-retained rehabilitation](https://norismedical.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/4-1-1024x580.jpg)
Anterior Zygomatic Implant Positioning
Posterior Zygomatic Implant Positioning
Pterygoid Implant Positioning: entering point on the buccal side of the ridge, 10-12 mm anterior to the maxillary tuberosity aiming towards the medial plate.
![[7] Implant Position 13 [8] Implant Position 23 [7] Implant Position 13 [8] Implant Position 23](https://norismedical.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/5-1024x580.jpg)
When analyzing the implant positioning it can be seen that the zygomatic bone in each position is relatively short (Between 9 to 11 mm) and the alveolar ridge excluding position 15 is completely atrophic, such a bone structure cannot support an individual zygomatic Implant. However, when all implants are connected by a rigid bar the construction is solid and can carry the load.
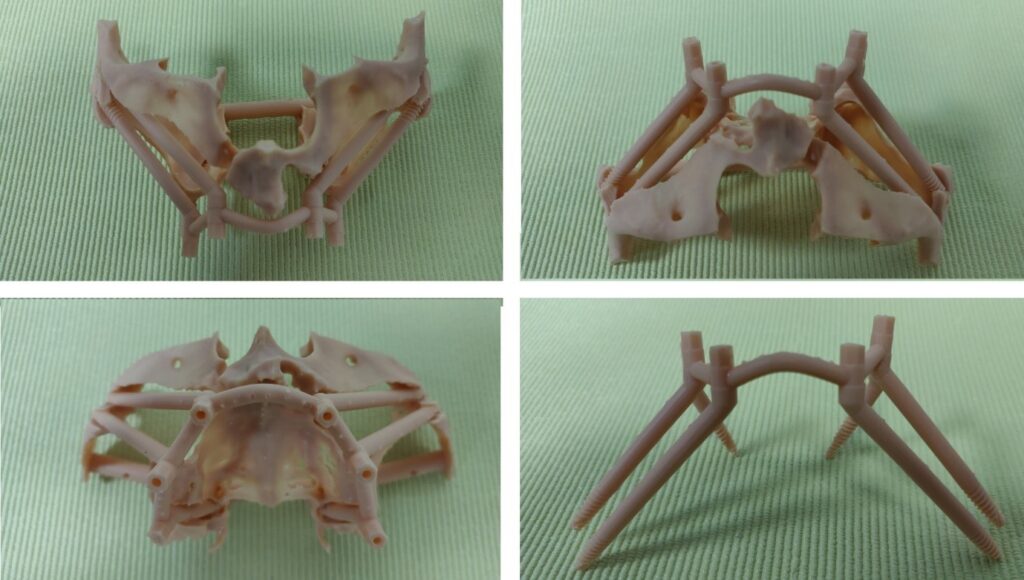
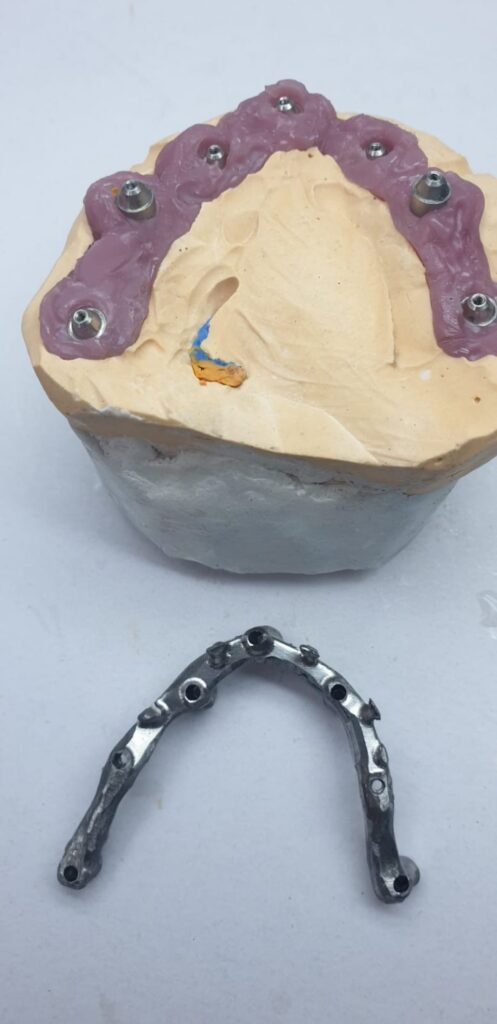
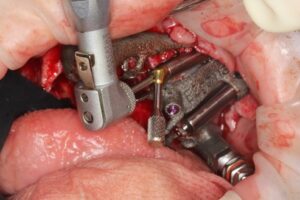
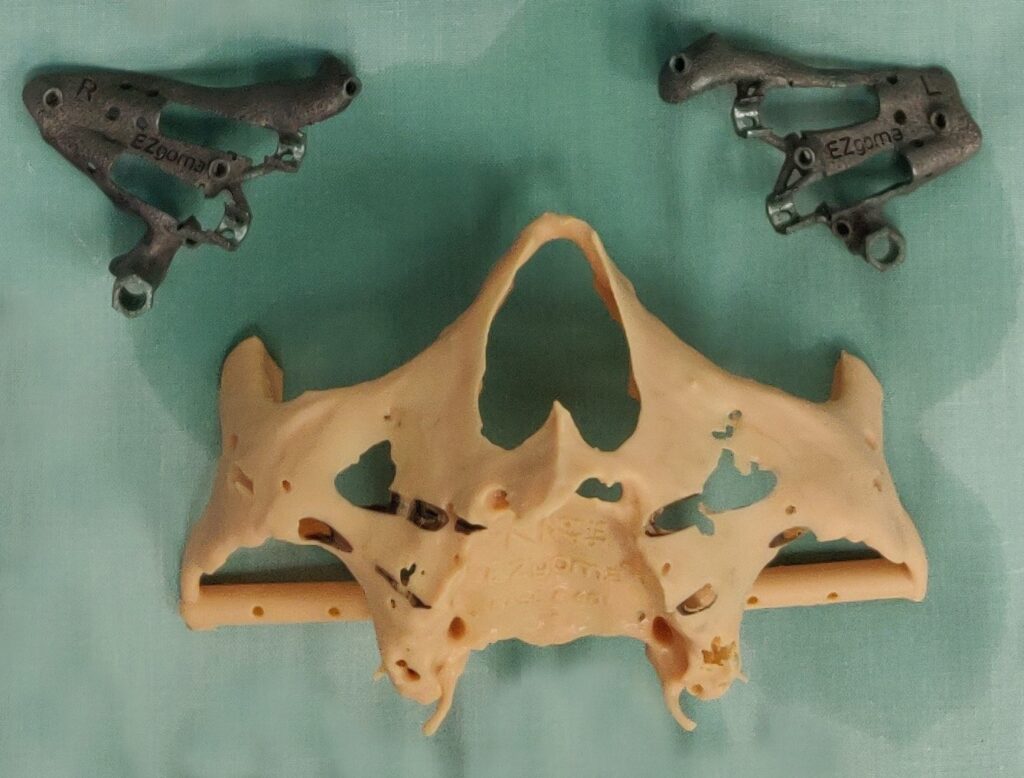
EZgoma guide:
Based on the implants positioning design, an individual guide is planned for each side, right and left, enabling a good insertion path with minimum undercuts. the guides enable positioning the implants through it to the correct position and prosthetic orientation.
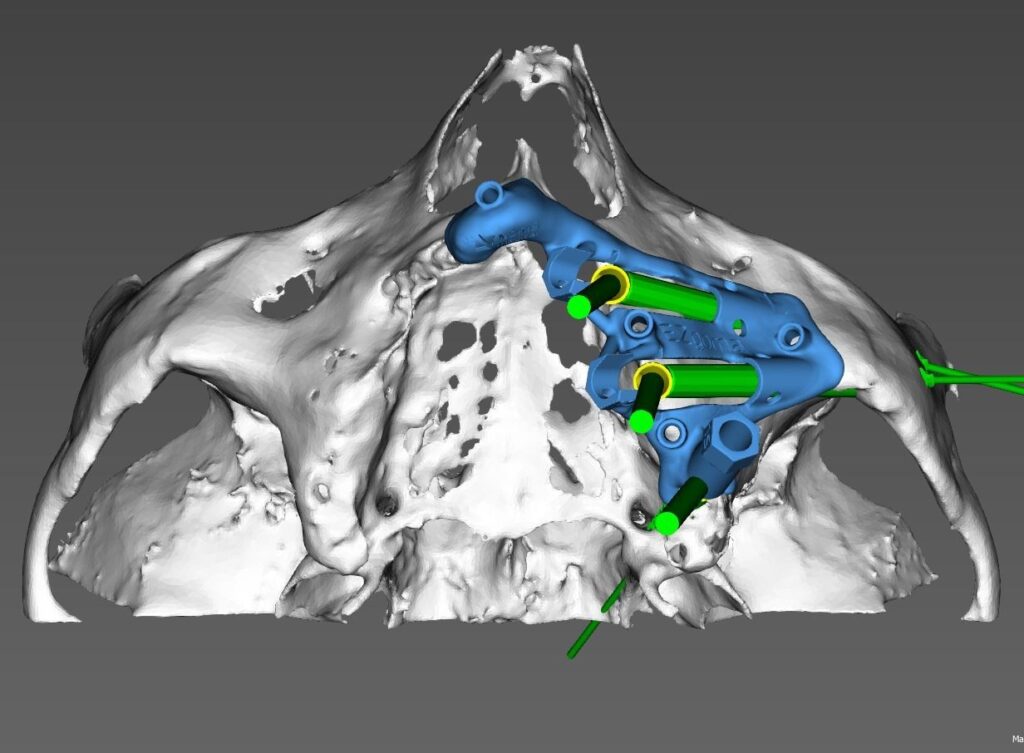
EZgoma® Titanium Surgery Guides
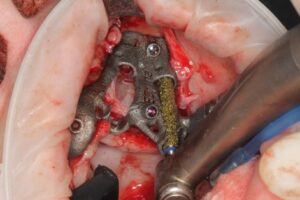
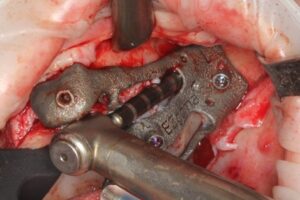
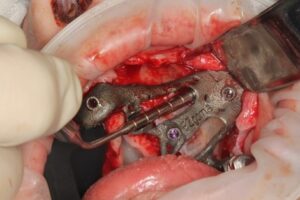
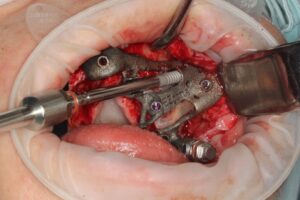
Surgical procedure